What is a SPACE Analysis?
Space analysis is an approach to strategic analysis used to develop a business strategy. SPACE is an acronym that stands for Strategic Position and Action Evaluation. The process for carrying out a SPACE Analysis is outlined below.
A SPACE analysis involves both an internal and external analysis.
External Analysis
The external environment is evaluated based upon:
-
Environmental Stability (ES) – Stability includes such factors as:
- technological change,
- inflation rate,
- demand volatility,
- price range of competitive products,
- price elasticity of demand, and
- pressure from the substitutes
-
Industry Attractiveness (IA) – Industry Attractiveness includes the following factors:
- growth potential,
- profit potential,
- financial stability,
- resource utilization,
- complexity of entering the industry,
- labor productivity,
- capacity utilization,
- bargaining power of manufacturers
Internal Analysis
The internal environment is evaluated based upon:
- Competitive Advantage (CA) – Competitive advantage includes the following factors:
- Market Share
- Product Quality
- Product Lifecycle
- Innovation Cycle
- Customer Loyalty
- Vertical Integration
- Financial Strength (FS) – Financial Strength includes the following factors:
- Return on investment,
- Liquidity,
- Debt ratio,
- Available versus required capital,
- Cash flow,
- Inventory turnover
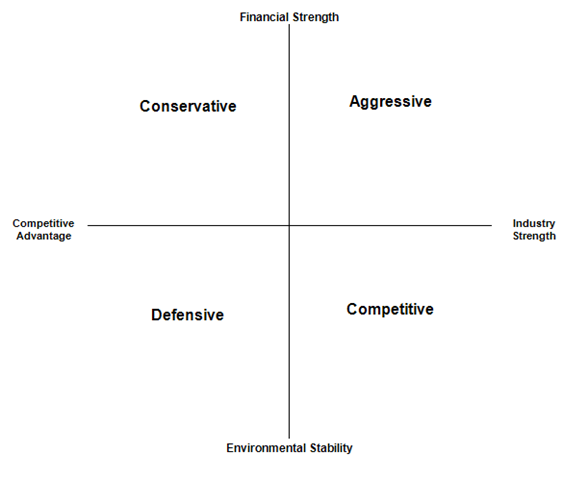
Each of these factors are assigned a value of 0-6 (or 0 through -6 for CA and ES). The average of these factor scores constitutes the value of the category. These values are plotted on a matrix with four quadrants.
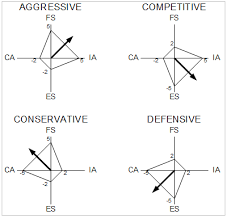
This image depicts SPACE Analysis in strategic management.
Each of the respective quadrants represents a strategic business behavior. The strategic behaviors are as follows:
- Aggressive position – Generally, this position is for a company in a stable industry within a protectable competitive advantage. Though new entrants into the market by competitors is a threat. Strategic objectives might include mergers or acquisitions, growing market share, or diversifying products/services.
- Competitive position – Generally, this position is for a financially stable company in an unstable environment. The company has some level of competitive advantage. There is generally opportunity in business combinations/partnerships, efficiency improvement, and a stronger cash flow.
- Conservative position – Generally, this position is for a highly stable company in a stable industry. Generally, the company has a strong market share and competitive position, but a low growth rate. There is opportunity through focusing on successful products and new product development.
- Defensive position – Generally, this position is for a company in a competitive industry that lacks a strong competitive advantage. The company must generally compete on efficiency and other cost-reduction methods. Though it should strongly consider pivoting or leaving the industry.
Related Topics
- How Strategies Arise
- Intended, Deliberate, Realized, and Emergent Strategies
- Management and Strategic Planning
- Mintzberg’s Schools of Strategic Development
- Design School
- Planning School
- Positioning School
- Entrepreneurial School
- Cognitive School
- Learning School
- Power School
- Culture School
- Environmental School
- Configuration School
- Mintzberg’s 5Ps of Strategy
- McKinseys 7s Model
- ***Industry Analysis to Build a Strategy***
- Strategic Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- SPACE Analysis
- Situational Analysis – 7C
- Competition Profile Matrix
- Stakeholder Analysis
- Stakeholder Mapping
- Resources and Capabilities
- VMOST
- Core Competency
- VRIO Analysis
- Value Chain Analysis
- Internal Factor Analysis
- Value Creation Index
- Minimum Efficient Scale
- PEST(LE) Analysis
- Industry Lifecycle Analysis
- Company Lifecycle – Definition
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Modes of Management
- External Factor Evaluation
- Strategy Implementation
- Eclectic Implementation Model
- Mintzberg’s Modes of Strategic Decision-Making
- Mintzberg’s Five Configurations
- Value Engineering
- Business Performance Measurement
- Benchmarking
- Balanced Scorecard
- Economic Value Added
- Activity-Based Management
- Quality Management
- Action Profit Linkage Model
- Business Activity Monitoring
- Gap Analysis
- Strategy Diamond
- BCG Growth-Share Matrix
- GE McKinsey Matrix
- Value Reporting Framework
- Pyrrhic Victory
