How does Relative Inflation Shifts Demand and Supply for a Currency?
If a country experiences a relatively high inflation rate compared with other economies, then the buying power of its currency is eroding, which will tend to discourage anyone from wanting to acquire or to hold the currency.
The below figure shows an example based on an actual episode concerning the Mexican peso. In 1986–87, Mexico experienced an inflation rate of over 200%. Not surprisingly, as inflation dramatically decreased the peso’s purchasing power in Mexico. The peso’s exchange rate value declined as well. The below figure shows that the demand for the peso on foreign exchange markets decreased from D0 to D1, while the peso’s supply increased from S0 to S1. The equilibrium exchange rate fell from $2.50 per peso at the original equilibrium (E0) to $0.50 per peso at the new equilibrium (E1). In this example, the quantity of pesos traded on foreign exchange markets remained the same, even as the exchange rate shifted.
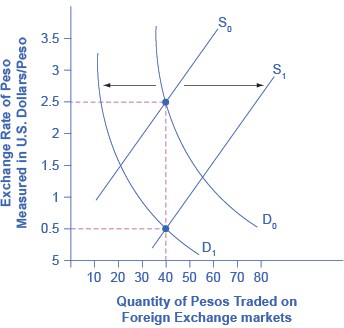
If a currency is experiencing relatively high inflation, then its buying power is decreasing and international investors will be less eager to hold it. Thus, a rise in inflation in the Mexican peso would lead demand to shift from D0 to D1, and supply to increase from S0 to S1. Both movements in demand and supply would cause the currency to depreciate. Here, we draw the effect on the quantity traded as a decrease, but in truth it could be an increase or no change, depending on the actual movements of demand and supply.
