How does a Minimum Wage act as a Price Floor in the Labor Market?
In contrast to goods and services markets, price ceilings are rare in labor markets, because rules that prevent people from earning income are not politically popular. There is one exception: boards of trustees or stockholders, as an example, propose limits on the high incomes of top business executives.
The labor market, however, presents some prominent examples of price floors, which are an attempt to increase the wages of low-paid workers. The U.S. government sets a minimum wage, a price floor that makes it illegal for an employer to pay employees less than a certain hourly rate.
Local political movements in a number of U.S. cities have pushed for a higher minimum wage, which they call a living wage. Promoters of living wage laws maintain that the minimum wage is too low to ensure a reasonable standard of living.
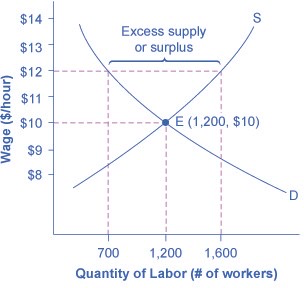
The U.S. minimum wage is a price floor that is set either very close to the equilibrium wage or even slightly below it. The vast majority of the U.S. labor force has its wages determined in the labor market, not as a result of the government price floor. However, for workers with low skills and little experience, like those without a high school diploma or teenagers, the minimum wage is quite important. In many cities, the federal minimum wage is apparently below the market price for unskilled labor, because employers offer more than the minimum wage to checkout clerks and other low-skill workers without any government prodding.
Economists have attempted to estimate how much the minimum wage reduces the quantity demanded of low-skill labor. A typical result of such studies is that a 10% increase in the minimum wage would decrease the hiring of unskilled workers by 1 to 2%, which seems a relatively small reduction. In fact, some studies have even found no effect of a higher minimum wage on employment at certain times and places—although these studies are controversial.
Let’s suppose that the minimum wage lies just slightly below the equilibrium wage level. Wages could fluctuate according to market forces above this price floor, but they would not be allowed to move beneath the floor. In this situation, the price floor minimum wage is nonbinding —that is, the price floor is not determining the market outcome. Even if the minimum wage moves just a little higher, it will still have no effect on the quantity of employment in the economy, as long as it remains below the equilibrium wage. Even if the government increases minimum wage by enough so that it rises slightly above the equilibrium wage and becomes binding, there will be only a small excess supply gap between the quantity demanded and quantity supplied.
These insights help to explain why U.S. minimum wage laws have historically had only a small impact on employment. Since the minimum wage has typically been set close to the equilibrium wage for low-skill labor and sometimes even below it, it has not had a large effect in creating an excess supply of labor. However, if the minimum wage increased dramatically—say, if it doubled to match the living wages that some U.S. cities have considered—then its impact on reducing the quantity demanded of employment would be far greater. As of 2017, many U.S. states are set to increase their minimum wage to $15 per hour. We will see what happens. The following Clear It Up feature describes in greater detail some of the arguments for and against changes to minimum wage.
Related Topics
- Labor Economics
-
Labor Market Equilibrium
- Labor Market
- Labor Market Equilibrium
- Labor Market Efficiency
- Price, Supply, and Demand in the Labor Market
- Equilibrium Wage
- Shifts in the Demand for Labor
- What Causes Shifts in the Supply Labor?
- How Technology affects Demand for Labor?
- Minimum Wage as a Price Floor in the Labor Market
- What is the First Rule of Labor Markets?
- Labor Demand in Perfectly Competitive Markets
- Imperfect Competition in Labor Markets
- Monopsony
- Oligopsony
- Labor Market Power of Employers
- What is the marginal Cost of Labor?
- Labor Market Power of Employees
- What is a Bilateral Monopoly in a Labor Market?
- Wage Elasticity of Labor Supply
- Equilibrium in Supply and Demand in Labor Markets
- Shifts in Supply and Demand in Labor Markets
