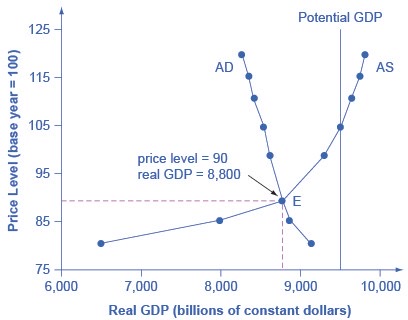
What is the Equilibrium Point for Aggregate Supply and Demand?
The intersection of the aggregate supply and aggregate demand curves shows the equilibrium level of real GDP and the equilibrium price level in the economy. At a relatively low price level for output, firms have little incentive to produce, although consumers would be willing to purchase a large quantity of output. As the price level rises, aggregate supply rises and aggregate demand falls until the equilibrium point is reached.
The equilibrium, where aggregate supply (AS) equals aggregate demand (AD).