How do changes in the expected rate of return shift demand and supply for a currency?
The motivation for investment, whether domestic or foreign, is to earn a return. If rates of return in a country look relatively high, then that country will tend to attract funds from abroad. Conversely, if rates of return in a country look relatively low, then funds will tend to flee to other economies. Changes in the expected rate of return will shift demand and supply for a currency. For example, imagine that interest rates rise in the United States as compared with Mexico. Thus, financial investments in the United States promise a higher return than previously. As a result, more investors will demand U.S. dollars so that they can buy interest-bearing assets and fewer investors will be willing to supply U.S. dollars to foreign exchange markets. Demand for the U.S. dollar will shift to the right, from D0 to D1, and supply will shift to the left, from S0 to S1, as the figure shows. The new equilibrium (E1), will occur at an exchange rate of nine pesos/dollar and the same quantity of $8.5 billion. Thus, a higher interest rate or rate of return relative to other countries leads a nation’s currency to appreciate or strengthen, and a lower interest rate relative to other countries leads a nation’s currency to depreciate or weaken. Since a nation’s central bank can use monetary policy to affect its interest rates, a central bank can also cause changes in exchange rates.
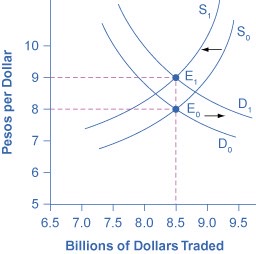
A higher rate of return for U.S. dollars makes holding dollars more attractive. Thus, the demand for dollars in the foreign exchange market shifts to the right, from D0 to D1, while the supply of dollars shifts to the left, from S0 to S1. The new equilibrium (E1) has a stronger exchange rate than the original equilibrium (E0), but in this example, the equilibrium quantity traded does not change.
Related Topics
- What Does it Mean to Dollarize
- Foreign Exchange Market
- Who Demands and Supplies Currency in a Foreign Exchange Market?
- Foreign Direct Investment
- Greenfield Investment
- Brownfield Investment
- Portfolio Investment
- Hedging
- Dealers in the Interbank Market
- Weak and Strong Currency
- Depreciation of Currency
- Appreciating and Depreciating Currency
- Exchange Rate
- Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER)
- Limited Flexibility Exchange Rate System
- Expectations about Future Exchange Rates Shift Demand
- Expected rate of return shift demand and supply for a currency
- Relative Inflation Shifts Demand and Supply for a Currency
- Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
- Relative Purchasing Power Parity
- Law of One Price
- Burgernomics
- Balassa-Samuelson Effect
- Arbitrage
- Tobin Tax
- Foreign Exchange Market
- Foreign Exchange Contract
- Arbitrage
- Hedge
- Why Central Banks Care About Exchange Rates
- How Do Exchange Rates Affect Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply?
- What Causes Exchange Rate Fluctuations?
- Exchange Rate Policy
- Fixed Exchange Rate
- Floating Exchange Rate
- Hard and Soft Peg
- What is a Merged Currency?
- Capital Control
- Exchange Stabilization Fund
