What is the Shutdown Point on The Cost Curve?
Shutting down can reduce variable costs to zero, but in the short run, the firm has already paid for fixed costs. As a result, if the firm produces a quantity of zero, it would still make losses because it would still need to pay for its fixed costs. Therefore when a firm is experiencing losses, it must face a question: should it continue producing or should it shut down?
When the firm is operating below the break-even point, where price equals average cost, it is operating at a loss so it faces two options: continue to produce and lose money or shutdown.
Which option is preferable? The one that loses the least money is the best choice.
The key reason is because price is above average variable cost. This means that at the current price the firm can pay all its variable costs, and have some revenue left over to pay some of the fixed costs.
So the loss represents the part of the fixed costs the firm can’t pay, which is less than the entire fixed costs.
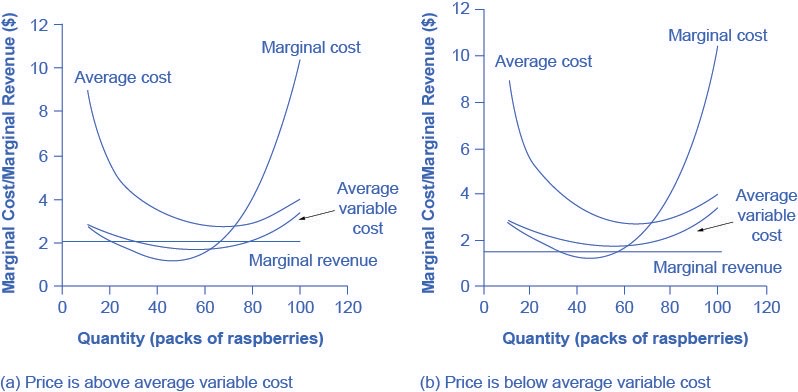
The intersection of the average variable cost curve and the marginal cost curve, which shows the price below which the firm would lack enough revenue to cover its variable costs, is called the shutdown point.
If the perfectly competitive firm faces a market price above the shutdown point, then the firm is at least covering its average variable costs. At a price above the shutdown point, the firm is also making enough revenue to cover at least a portion of fixed costs, so it should limp ahead even if it is making losses in the short run, since at least those losses will be smaller than if the firm shuts down immediately and incurs a loss equal to total fixed costs.
However, if the firm is receiving a price below the price at the shutdown point, then the firm is not even covering its variable costs. In this case, staying open is making the firm’s losses larger, and it should shut down immediately. To summarize, if:
- price < minimum average variable cost, then firm shuts down
- price > minimum average variable cost, then firm stays in business
