What is Contractionary Fiscal Policy?
Fiscal policy can also contribute to pushing aggregate demand beyond potential GDP in a way that leads to inflation.
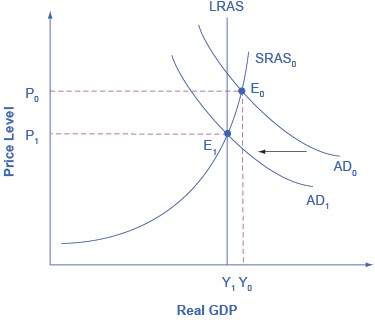
The graph below shows, a very large budget deficit pushes up aggregate demand, so that the intersection of aggregate demand (AD0) and aggregate supply (SRAS0) occurs at equilibrium E0, which is an output level above potential GDP. Economists sometimes call this an “overheating economy” where demand is so high that there is upward pressure on wages and prices, causing inflation. In this situation, contractionary fiscal policy involving federal spending cuts or tax increases can help to reduce the upward pressure on the price level by shifting aggregate demand to the left, to AD1, and causing the new equilibrium E1 to be at potential GDP, where aggregate demand intersects the LRAS curve.
The economy starts at the equilibrium quantity of output Y0, which is above potential GDP. The extremely high level of aggregate demand will generate inflationary increases in the price level. A contractionary fiscal policy can shift aggregate demand down from AD0 to AD1, leading to a new equilibrium output E1, which occurs at potential GDP, where AD1 intersects the LRAS curve.
Again, the AD–AS model does not dictate how the government should carry out this contractionary fiscal policy. Some may prefer spending cuts; others may prefer tax increases; still others may say that it depends on the specific situation. The model only argues that, in this situation, the government needs to reduce aggregate demand.
Related Topics
- What is Government Spending?
- Autonomous Spending
- Autonomous Consumption
- Fiscal Policy
- Expansionary Fiscal Policy
- Contractionary Fiscal Policy
- Progressive vs Regressive Tax
- Marginal Tax Rates
- Proportional Tax
- Trickle Down Theory
- Discretionary Fiscal Policy
- Automatic Stabilizers
- Effects of Discretionary Policy (Interest Rates & Lags)
- Crowding Out Effect
- National Debt
- Government Borrowing
- Golden Rule
- Ricardian Equivalence
- Balanced Budget – Deficit and Surplus
- National Debt
- Standardized Employment Budget
- Deficit Hawk
- Austerity
- Twin Deficits
- Fiscal Policy and the Aggregate Supply and Demand Curve
- Stabilization Policy
- Robin Hood Effect
- Ricardo Barro Effect
- Automatic Stabilizers
- Standardized Employment Budget
- How Does Fiscal Policy Affect Interest Rates?
- Crowding Out
- Types of Lag in Fiscal Policy
- Temporary and Permanent Fiscal Policy
- Limitations of Fiscal Policy?
- How Politics Affects Discretionary Fiscal Policy
- Government Borrowing
- National Savings and Investment Identity
- Debtor Nation
- Fiscal Policy Affects Trade Balances
- Twin Deficits
- Exchange Rates Affect Budget and Trade Deficits
- What are the risks of chronic large deficits in the United States?
- How Fiscal Policy Can Affect Trade Imbalances
- Government Borrowing Affect Private Savings
- Ricardian Equivalence
- Fiscal Policy Affects Investment and Economic Growth
- Crowding Out of Physical Capital Investment?
- How Does Government Borrowing Affect Interest Rates in Financial Markets?
- Government Investment in Physical Capital
- Public Investment in Human Capital
- Fiscal Policy Can Affect Technology Development
- Economic Cycle or Business Cycle
- Business Cycle Indicator
- Peak and Trough
- Recession and Depression
- Hard Landing vs Soft Landing
- Economic Bubble
- Boom and Bust Cycle
- Great Depression
- Baby Boomer Age Wave Theory
- Skyscrapper Effect (Economics)
- V-Shaped Recovery
- W-Shaped Recovery
- U-Shaped Recovery
- Kondratieff Wave Cycle
- Contagion
- Feedback Rule Policy
- American Customer Satisfaction Index
- CNN Effect
- Bureau of Economic Analysis
- Business Starts Index
- American Recover and Reinvestment Act
- Abenomics
- Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008
- Commodity Credit Corporation
- Humphrey Hawkins Act
- Real Economic Growth Rate
- Fox-Trot Economy
- Stagnation
- Neoclassical Growth Theory
- Exogenous Growth Theory
- Endogenous Growth Theory
- New Growth Theory – Explained
- Classical Growth Theory – Explained
- Real Economic Growth Rate – Explained
- Plutonomy
